FEA Software Predicts Material Response to Repeated Snap Fits
Improved finite-element modeling accounts for viscoelastic response to multiple stress-strain cycles.

Designing parts with snap fits present a particular challenge because of the repeated cyclic loading and unloading. During such cycles, the viscoelastic nature of thermoplastic materials determines how the bouncing back to “normal” occurs—and how it varies with time over multiple stress-strain cycles.
That’s part of the challenge that faced of Copenhagen, Denmark, a world leader in insulin self-injection pens. These pens are small, but they are precision instruments with a number of complex parts that must work in perfect coordination. Some pens are durable, containing a replaceable drug cartridge, while disposable ones come pre-filled with a drug. Injection typically involves twisting a short needle onto the pen, turning a dial to the required dose, and pushing a button to deliver the medication under the skin. After a given number of doses is injected, either the cartridge is replaced (for a durable device) or the pen is discarded (if a disposable version). In either case, audible clicks occur at key stages of the procedure, reassuring patients that they are engaging the device correctly at each step. But every one of those reassuring clicks represents a challenge to the design engineers. So do the clicks the patient never hears—those that occur during assembly of the pens in production.
To integrity of their designs, Novo Nordisk’s Device Simulation department rely on computer simulation with Abaqus finite-element analysis (FEA) software from Simulia, an application of of France (U.S. headquarters in Providence, R.I.). “Over a decade ago, I and my colleagues explored a number of commercial software codes,” says Torben Strøm Hansen, principal scientist in the Device R&D division of Novo Nordisk. “We chose Abaqus because it was a well-integrated solution that could model the nonlinear behavior of the fine details our designs correctly, including the high number of interfaces in contact.”
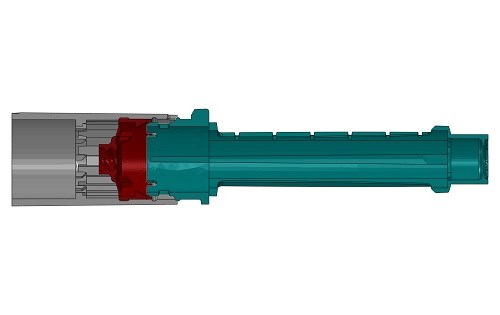
CAD model of insulin pen components. Gray and red parts snap fit onto the green part.
Besides modeling viscoelastic response to repeated snap fits over time, the designers had to predict the behavior of the materials in different environments, including elevated temperatures, even though the pens are assembled from different materials. And, some materials may contain carbon or glass fibers that show anisotropic behavior, which can be hard to predict. Even just sitting on a pharmacy shelf or in a consumer’s medicine cabinet, the materials are prone to creep and relaxation over time at rates that can vary with temperature.
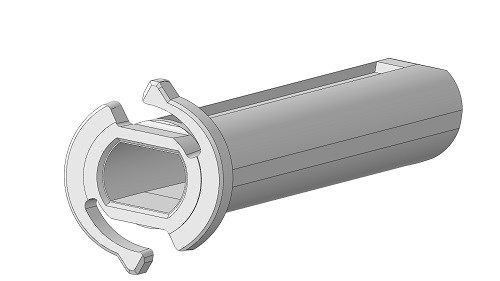
Injection molded ratchet component from a medical device used by Novo Nordisk for a snap-fit benchmark study.
Hansen’s team at Novo Nordisk is now using the “parallel rheological framework” methodology available in Abaqus to model polymers’ nonlinear viscoelasticity with greater accuracy than before. The framework makes use of an arbitrary number of viscoelastic networks and an elastic equilibrium network to create a nonlinear model to predict and track changes in the internal structural networks of a polymer as it responds to repeated cyclic snap-fit loads. “Having material models incorporating time-dependent viscous behavior is very important for our work,” says Hansen. “We’re now able to simulate both creep and relaxation with Abaqus.” Since every type of polymer shows a different response to temperature, load, etc., the team continues to explore ways to identify the characteristics of different polymer networks.
Not only are such advanced models useful to designers in fine-tuning the latest insulin pen configuration, the data can help in manufacturing processes at the factory. “We have a process-simulating capability, through , for which Abaqus has an interface. This allows us to input the stress fields that result from the injection molding process right into our models. As a result, we have greater insight into our manufacturing process and are more able to design parts that have very low levels of residual stress in critical regions.”
Related Content
How to Achieve Simulation Success, Part 2: Material Characterization
Depending on whether or not your chosen material is in the simulation database — and sometimes even if it is — analysts will have some important choices to make and factors to be aware of. Learn them here.
Read MoreSoftware Suite Creates Integrated Workflows for Optimizing Moldmaking
Eastec 2025: The HxGN Mould and Die Suite includes VISI, WORNC, NCSIMUL and datanomix tools to provide an integrated workflow from design/engineering to manufacturing and automation.
Read MoreRead Next
For PLASTICS' CEO Seaholm, NPE to Shine Light on Sustainability Successes
With advocacy, communication and sustainability as three main pillars, Seaholm leads a trade association to NPE that ‘is more active today than we have ever been.’
Read MoreSee Recyclers Close the Loop on Trade Show Production Scrap at NPE2024
A collaboration between show organizer PLASTICS, recycler CPR and size reduction experts WEIMA and Conair recovered and recycled all production scrap at NPE2024.
Read More