Antimicrobial Based on Elemental Zinc Reduces Coronavirus on Surfaces by Up to 99%
Parx Materials’ Saniconcentrate expected to be a strong and safe tool in preventing the future spread of viruses.
Dutch/Italian technology start-up , based in Rotterdam, which first launched its patented Saniconcentrate antimicrobial technology in 2014, has now proven that its additive technology reduces Covid-19 virus without harmful toxins on surfaces by up to 99% in 24 hours. Unlike other antimicrobial options, it achieves this without biocides, leaching or harmful side effects, creating a breakthrough option for applications like touch surfaces in public areas, medical devices or food contact applications.
The additive had already been shown to allow plastics manufacturers to create self-sanitizing products with an antibacterial property of up to 99% within 24 hours, as determined according to ISO22196 with gram positive Staphylococcus aureus and gram negative Escherichia coli bacteria. The latest information is said to prove that Saniconcentrate will be a strong and safe tool in preventing the spread of viruses in the future. With Saniconcentrate, Parx Materials has created a way to make plastic intrinsically resistant to bacteria and viruses. The additive is homogenously incorporated into plastics to create an ‘immune system’ inherent to the material. The technology makes use of the one of the body’s most abundant trace elements: zinc.

Antimicrobial technologies have historically used biocides, such as silver or copper, to destroy microorganisms. While this method may effectively destroy bacteria and viruses, it can lead to toxic substances leaching out of the material, contaminating the products or surfaces it is trying to protect, as well as contaminating the environment and making recycling a more challenging task. In addition to relying on finite resources to work, bacteria and viruses tend to become resistant to biocides over time, reducing the biocides’ efficacy. Making bacteria viruses stronger so they become more difficult to battle and cause a bigger threat in the future.
Typically, bacteria and viruses attach to surfaces in order to sustain themselves over a long period of time. Inspired by the defense mechanisms of the human body, the technology of Parx Materials works by mimicking the physical characteristics of the human skin. Using trace element zinc abundantly found in the body, biocompatible Saniconcentrate has been shown to prevent bacteria and viruses from adhering to surfaces, causing them to run through their usual lifecycle and die within hours. This ecological approach of dealing with germs can be seen as a natural way to keep bacteria and viruses at bay, instead of just killing them and inducing resistance. The technology is currently in use in major supermarkets and has shown outstanding results in medical trials.
Carried out by an authorized laboratory, the new study identifies the development of the amount of Covid-19 virus on plastic surfaces made with the Saniconcentrate additive. The test was carried out in accordance with ISO 21702:2019 “measure of antiviral activity on plastics and other non-porous surfaces”. After 24 hours, the treated sample saw a 99% reduction in the virus.
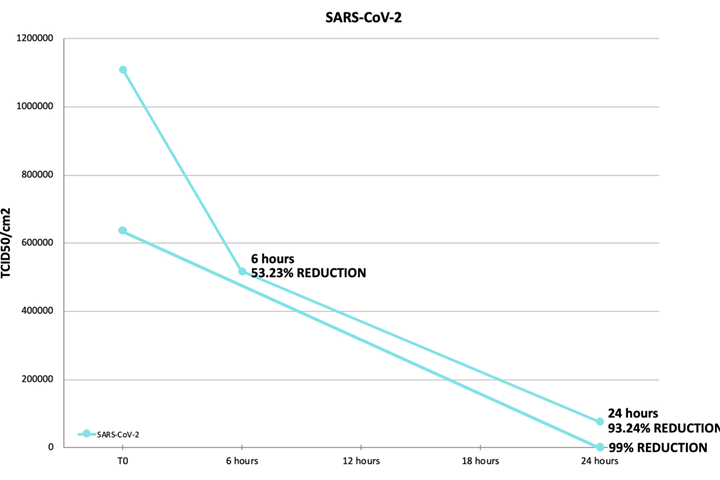
A second test on a different material made with Saniconcentrate, found a 53.23% reduction in Covid-19 virus after just six hours and a 93.24% reduction after 24 hours. This proves definitively that Saniconcentrate protects surfaces against coronavirus and therefore its spread.
Said Parx Materials’ CEO Michaël van der Jagt, “Today’s struggles against the Covid-19 pandemic and antibiotic-resistant superbugs show that innovation is needed when it comes to antimicrobial materials. The test results showing a 99% reduction in coronavirus on Saniconcentrate treated surfaces confirms its ability to help us return to normal life using a safe and ecological approach.”
Parx Materials is currently looking for investment to further accelerate its scale up.
Related Content
Insight Polymers & Compounding Unveils New Conductive Products Line
The new conductive products line will also be produced for injection molding and extrusion.
Read MoreCalcium Carbonate From Carbon Capture for Brighter Plastics and Greener Steel
CarbonFree is converting steel slag and blast furnace exhaust into an important plastic compounding additive.
Read MoreAt NPE2024, Follow These Megatrends in Materials and Additives
Offerings range from recycled, biobased, biodegradable and monomaterial structures that enhance recyclability to additives that are more efficient, sustainable and safer to use.
Read MoreRiverdale Global Showing Latest Innovations and New Satellite Location in Wisconsin
NPE2024: Live demos of updated RGS controller are among the highlights at its Wisconsin facility that will house the ‘new’ color R&D lab.
Read MoreRead Next
People 4.0 – How to Get Buy-In from Your Staff for Industry 4.0 Systems
Implementing a production monitoring system as the foundation of a ‘smart factory’ is about integrating people with new technology as much as it is about integrating machines and computers. Here are tips from a company that has gone through the process.
Read MoreLead the Conversation, Change the Conversation
Coverage of single-use plastics can be both misleading and demoralizing. Here are 10 tips for changing the perception of the plastics industry at your company and in your community.
Read More












